Introduction#
The goal of this infrastructure is to allow devices on my LAN, or remotely through VPN, to securely access my self-hosted services, such as Gitea or Paperless NGX.
To achieve this, I rely on several open-source tools, each with a well-defined role:
- pfSense : acts as the main gateway, DNS, and DHCP server.
- Nginx : reverse proxy for all internal services.
- Proxmox : hypervisor hosting all virtual machines.
- Pi-hole : DNS for internal traffic.
Virtualization Layer : Proxmox VE#
Architecture#
My current setup runs on a single Proxmox node hosted on an AMD mini-PC with two network interfaces and five virtual machines. Network topology:
- Network Device 0 : Ethernet port connected to the home router (Internet access).
- Network Device 1 : Not connected yet (reserved for future VLANs).
- Linux Bridge 0 (vmbr0) : Connected to Network Device 0 → 192.168.1.0/24.
- Linux Bridge 1 (vmbr1) : Connected to Network Device 1 → 192.168.100.0/24.
- VM Infra : Connected only to vmbr1.
- VM pfSense : Connected to both vmbr0 and vmbr1.
- VM Dev
- VM Media
Network Layer : pfSense and DNS#
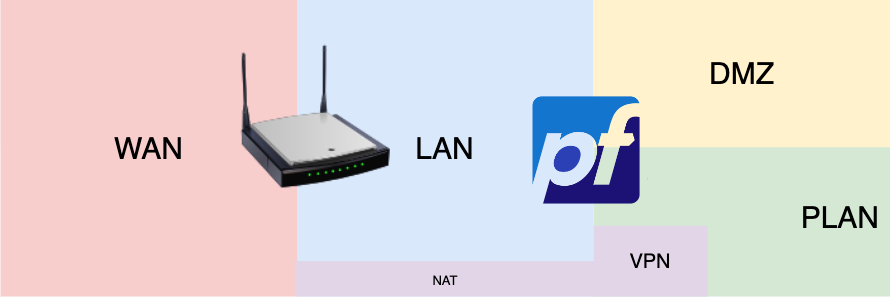
pfSense#
pfSense is the central piece of my network, managing traffic between different bridges and networks in Proxmox. Interfaces:
- LAN : Linked to Linux Bridge 0 (home network).
- PLAN : Linked to Linux Bridge 1 (internal infrastructure).
- DMZ : Reserved for exposed services (not linked yet).
- VPN1 : NATed connection to the home router.
DNS setup#
- PLAN DNS: Pi-hole runs on the Infra VM and acts as the main DNS resolver for the PLAN network.
- LAN DNS: pfSense DNS Resolver is used on the LAN side. The home router uses pfSense’s IP address as its primary DNS server, which allows all LAN devices to resolve internal hostnames.
Application Layer : Nginx#
Deployment and Automation#
- Nginx and Certbot are deployed using Ansible in Docker containers with a GitOps approach.
- Configuration files are stored in Git, and Semaphore automatically runs the deployment playbooks (on a schedule via cron for certbot and in CI/CD via webhook for nginx).
- Ansible Vault securely stores credentials
- Shared Docker volumes with nginx container are used for SSL certificates generated by Certbot.
Gateway Logic#
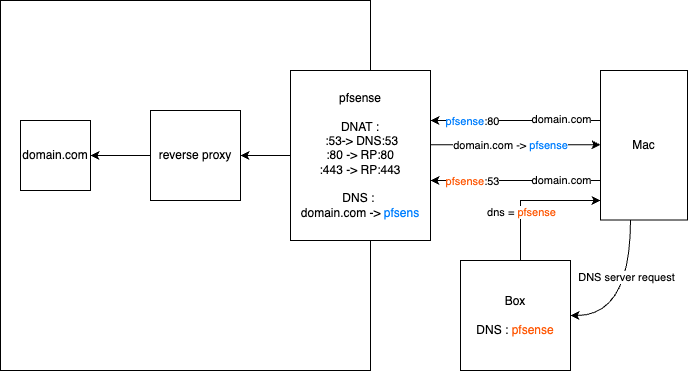
Because my home router doesn’t allow direct routing to another network besides WAN, pfSense uses NAT to forward requests properly.
Example: accessing gitea.quentinmarques.com
- The home router uses pfSense as its DNS server.
- A client requests gitea.quentinmarques.com, pfSense resolves it to its own LAN IP.
- pfSense performs DNAT, forwarding port 443 on its LAN interface to port 443 of the VM Infra inside the PLAN network.
- SNAT ensures the response packets are properly returned to the requesting device.
- Finally, Nginx on the VM Infra routes the request to the VM:PORT hosting Gitea.
Lessons Learned#
- Gained hands-on experience with pfSense, Proxmox, and Nginx.
- Deepened understanding of networking concepts such as NAT, DNAT, and SNAT through practical configuration and troubleshooting.
- Improved skills in technical documentation and diagram creation, helping to structure ideas clearly and simplify future maintenance.
Next Steps#
- VLAN segmentation : Improve isolation between networks and prepare for scalability.
- Start DMZ with nginx and fail2ban : Add brute-force protection for exposed services.
- Terraform for Proxmox : Automate VM provisioning and configuration.
